Now Reading: How the Global Supply Chain Affects Daily Prices
-
01
How the Global Supply Chain Affects Daily Prices
How the Global Supply Chain Affects Daily Prices
Most people rarely think about how a product reaches their home — from vegetables to smartphones, every item’s price is shaped by a vast global network known as the supply chain. When this system faces disruption, the effects ripple across economies and into household budgets. From shipping delays to higher fuel costs, supply chain instability directly impacts what consumers pay in stores and online.
The Invisible Web Behind Every Product
A global supply chain connects manufacturers, suppliers, transporters, and retailers across continents. A single product can pass through multiple countries before reaching the shelf. For instance, raw materials might come from Africa, be assembled in China, and sold in India. This complex web keeps the global economy running smoothly, but any break — like a port blockage or shortage of raw materials — can cause prices to jump unexpectedly.
Pandemic Lessons and Ongoing Disruptions
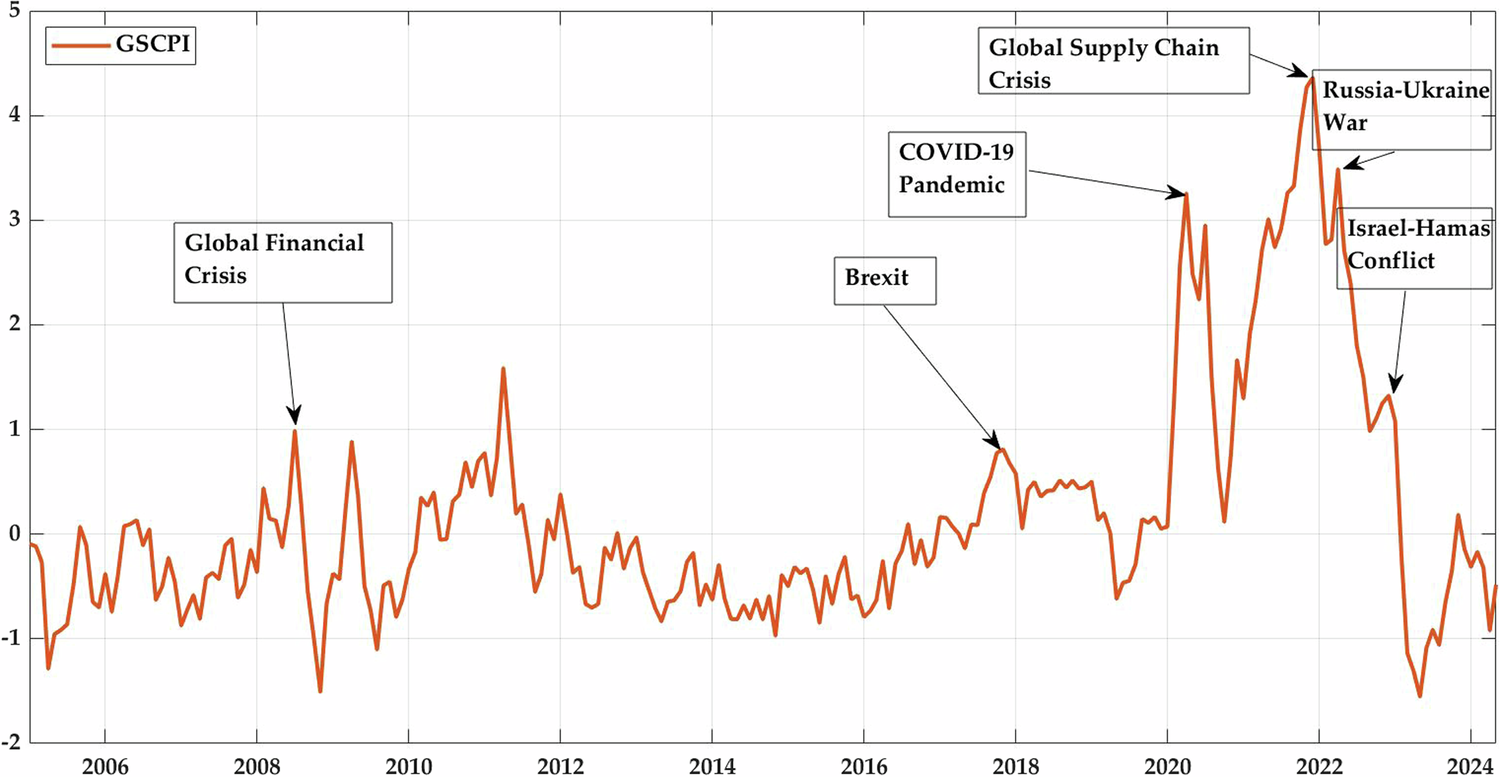
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed how fragile this system truly is. Lockdowns, labor shortages, and transport restrictions disrupted global trade routes. Factories shut down, shipping containers piled up at ports, and demand patterns shifted drastically. Even as the world reopened, many industries struggled to return to pre-pandemic efficiency. The aftereffects — from higher freight costs to semiconductor shortages — continue to affect prices of electronics, cars, and even groceries.
India’s Position in the Chain
India plays a key role in the global supply chain — both as a manufacturing hub and a consumer market. Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities depend heavily on imports for essential items such as edible oils, electronic goods, and machinery parts. When international shipping costs rise or trade routes are disrupted, these additional expenses often trickle down to Indian consumers. A minor fluctuation in global crude oil prices, for example, can increase transport costs, leading to higher prices for vegetables or packaged foods in local markets.
The Impact of Currency Fluctuations
Global trade also depends on currency values. A weaker rupee makes imports more expensive, pushing up the cost of foreign goods. This is especially relevant in India’s urban centers where imported electronics, luxury items, and fuel dominate consumption patterns. The rise in import costs eventually leads to inflation — meaning everyday items from mobile phones to petrol cost more than they did months before.
How Companies Pass on Costs
Businesses facing increased supply chain expenses often pass them to consumers. For instance, when raw material prices rise, manufacturers increase their selling prices to protect profit margins. Retailers then adjust their pricing to balance inventory costs. This chain reaction is visible across sectors — from automobiles to packaged foods — making “price rise” a common term in every household discussion.
Local Solutions for Global Problems
To reduce dependency on volatile international systems, countries including India are focusing on self-reliance. Government initiatives promoting domestic manufacturing and logistics infrastructure aim to make local industries less vulnerable to global disruptions. The “Make in India” push and the rise of regional supply chains are part of this strategy, encouraging businesses to source and produce locally wherever possible.
What It Means for Consumers
For everyday consumers, understanding the link between supply chains and prices can explain sudden changes at the checkout counter. Whether it’s the rising cost of tomatoes, smartphones, or petrol, the reason often lies thousands of miles away — in a delayed shipment, a conflict zone, or a factory closure.
In a globalized world, the supply chain acts as the hidden backbone of the economy. When it runs smoothly, prices stay stable. When it falters, households feel the strain. The next time an item seems costlier than before, it might not just be inflation — it could be the world’s complex supply chain quietly reshaping the price you pay.